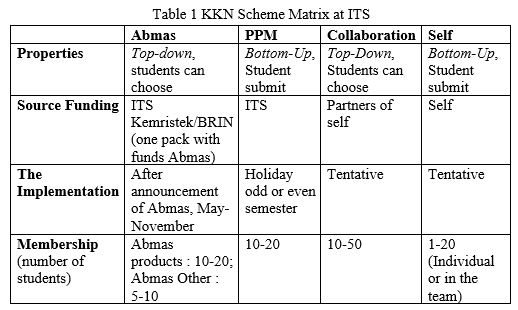
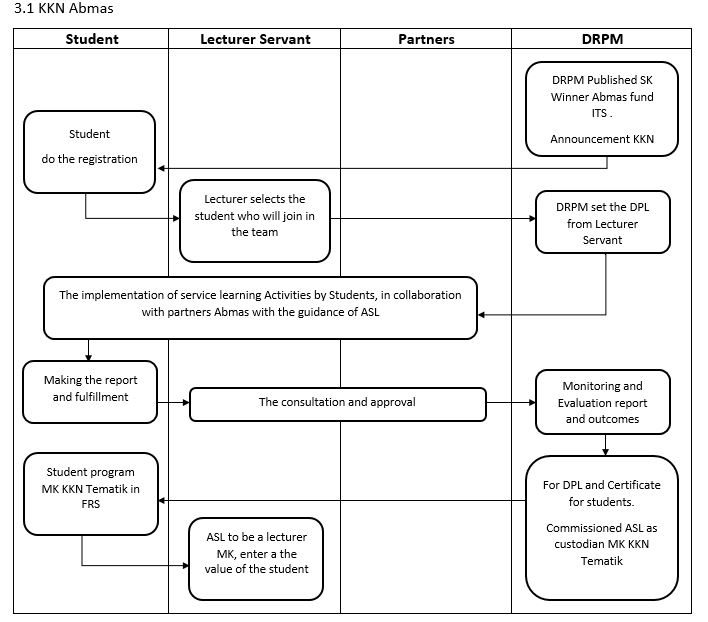
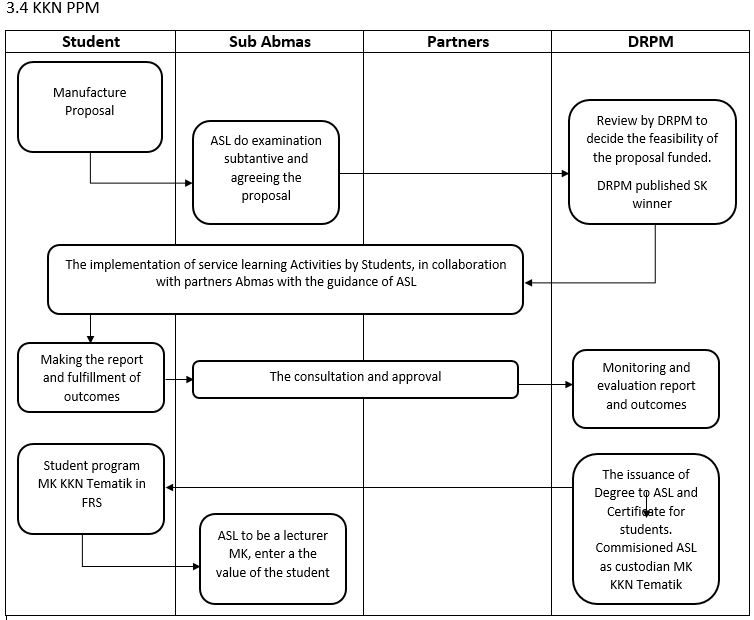
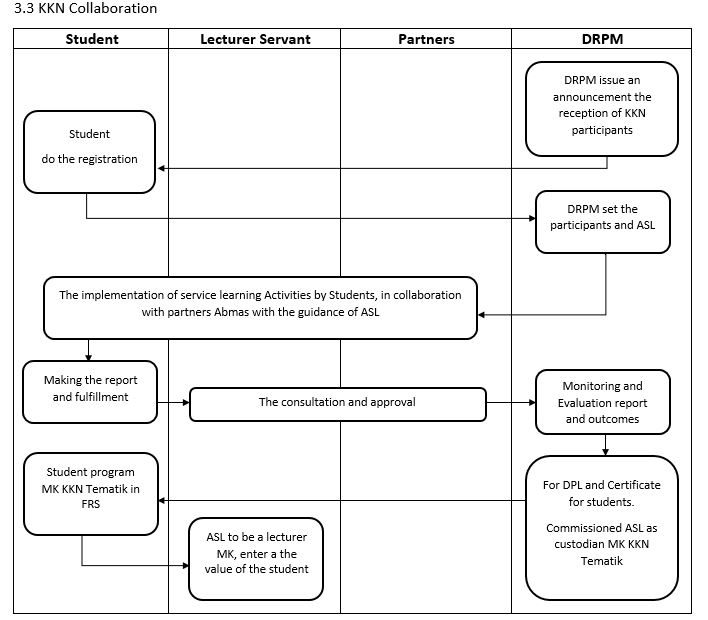
3.1 Announcement Stage
The thematic KKN management cycle begins with the announcement of the acceptance of the Thematic KKN proposal online by the ITS DRPM. The announcement of the acceptance of the proposal is attached with the Thematic KKN Implementation Guidebook.
3.2 Registration Stage
Registration of proposals is carried out by students / groups of students through an online registration system to DRPM ITS by following the thematic KKN participation requirements.
3.3 Selection/Appointment Stage
The registration/proposal selection is carried out by the ITS DRPM assessment team online. At this stage, it is possible to appoint a team of Field Supervisors (DPL) to students who can take the Thematic KKN. Students who pass this selection can then follow the following processes.
3.4 Determination Stage
The Thematic KKN team consisting of DPL and students is determined through a decree from the ITS DRPM and given a letter of assignment to carry out Thematic KKN.
3.5. Implementation Stage
a) Thematic KKN activities consist of debriefing, field activities and reporting that must be completed for 2-3 months.
b) The duration of field activities in the target area or with the target community is a minimum of 140 hours or the equivalent of 3 weeks.
c) Field activities can be carried out online, offline or a combination of online and offline (hybrid).
d) Thematic KKN is guided by at least 1 Field Supervisor (DPL)
e) Thematic KKN is carried out individually or in groups and in collaboration with the community and/or carried out in the village/kelurahan.
3.6 Monitoring Stage
DRPM ITS conducts monitoring and evaluation of the implementation of Thematic KKN through the monitoring team. The monitoring team reports the results of monitoring and evaluation of the implementation to DRPM ITS. DRPM ITS then makes the evaluation results as feedback for continuous improvement of quality assurance.
3.7 Reporting Stage
a. The Thematic KKN Team Leader must submit: final report, activity logbook, activity video (2-5 minutes) uploaded to the ITS DRPM Youtube account, and evidence of media coverage (whether in the form of news, opinions or others)
b. DPL provides an assessment of students participating in Thematic KKN based on the provisions of the ITS DRPM. The results of this student assessment will be sent to the Academic Division to be recorded in the relevant participating student scores.